SAML
OpenID Connect
Message format
XML
JSON
API
SOAP
REST
Website authentication
![]()
![]()
Mobile applications
![]()
User consent
![]()
Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) and OpenID Connect (OIDC) are the most widely used federation protocols for web based single sign-on, and Kantega SSO Enterprise supports both. Both protocols are secure and works across remote networks, and they allow you to login to your Atlassian Application through an identity provider service, such as AD FS, AzureAD, Google, Okta, AWS, Keycloak, and many more.
The first thing to understand is that OAuth 2.0 is an authorization framework, not an authentication protocol.
OpenID Connect (OIDC) is an authentication protocol and an identity layer built on top of OAuth 2.0. It does everything OAuth does. Plus authentication. It uses JSON Web Tokens (JWT), called an ID token, to provide authentication information.
SAML is independent of OAuth, relying on an exchange of messages to authenticate in XML SAML format, as opposed to JWT. Even though OpenID is a modern alternative to SAML, SAML is still the most common choice for SSO for most enterprise applications.
The table below summarizes differences between SAML and OIDC:
SAML | OpenID Connect | |
|---|---|---|
Message format | XML | JSON |
API | SOAP | REST |
Website authentication |
|
|
Mobile applications |
| |
User consent |
| |
SAML rely on browser redirects, which does not work well in native mobile apps. However, note that many mobile apps, including the Jira Server Mobile and Confluence Server Mobile apps, are built using embedded web views. Here SAML will work perfectly fine.
Because OIDC is a layer placed upon the OAuth framework, OpenID Connect can provide a built-in layer of authorization, which prompts a user to first consent to what the service provider can access. Even though SAML can provide consent flow, it does this through hard-coding done by the developer, instead of having it as a standard in its protocol.
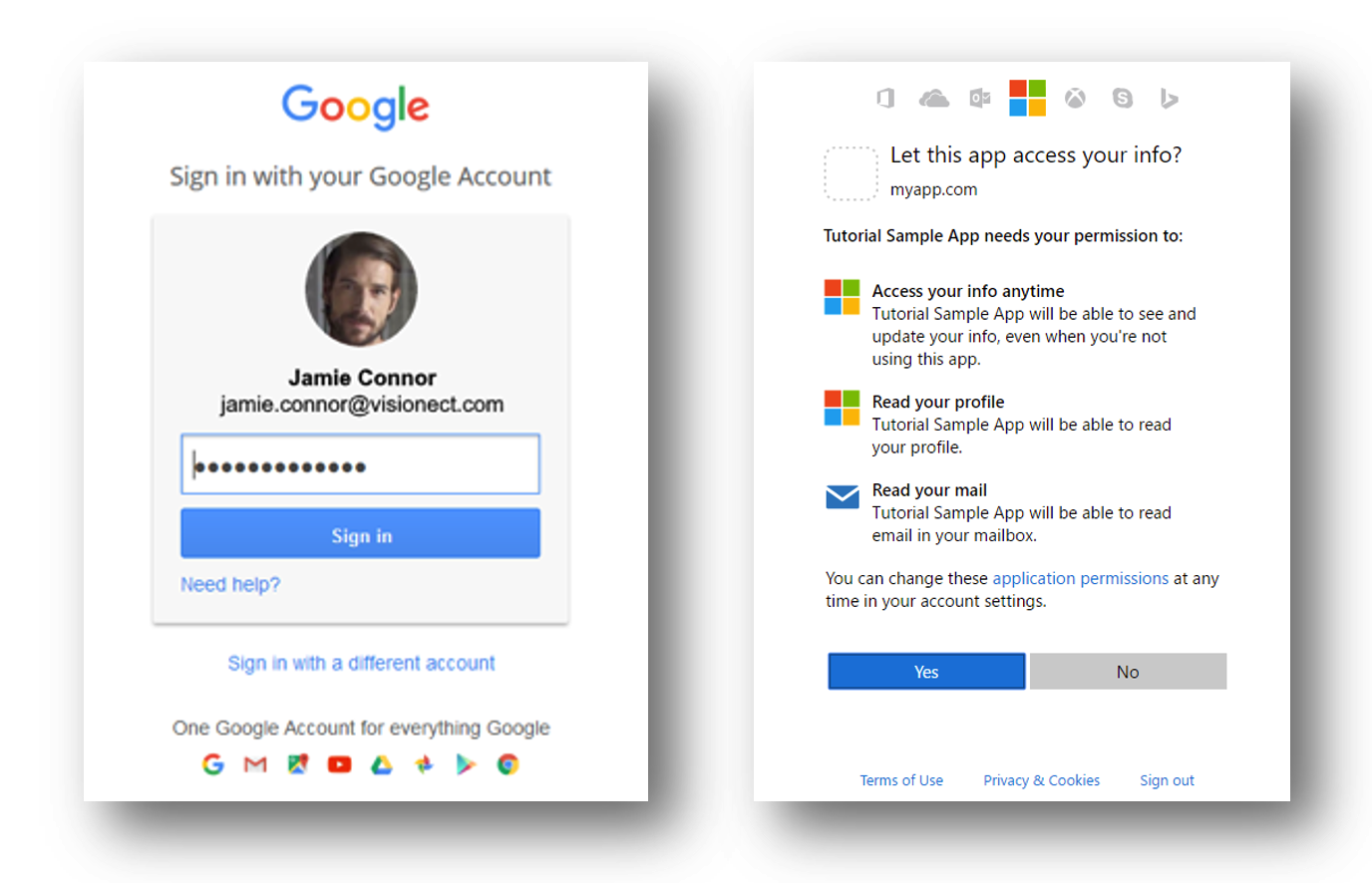
The login screenshots above shows how such user consent is requested. First the user is authenticate, and then a consent screen is shown, requesting consent to retrieve personal user data.
Both SAML and OIDC providers can be configured to make use of Multi-factor Authentication (MFA). More info about how to setup an identity provider in Kantega SSO Enterprise and enforce MFA.
Kantega SSO Enterprise allows you to setup multiple identity providers concurrently, and use SAML and OIDC in combination with other authentication mechanism such as Kerberos and traditional username / password logins. More info about how to configure multiple authentication mechanisms and automatically route users based on user directory, group and domain associations.